
4. Chemical Reactions
(Last Updated 01/28/2024, 15:30 MST)
Brown Chapter 3 Stoichiometry PowerPoint
Brown Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solution PowerPoint
4.1 Introduction for Reactions

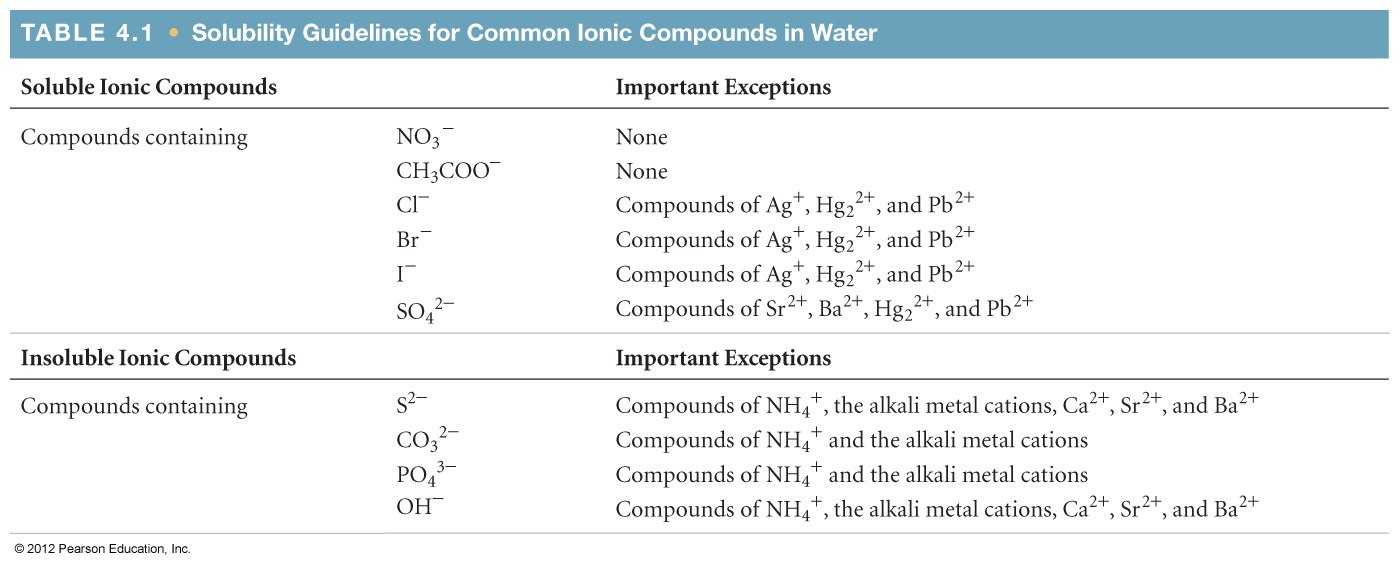
4.2 Net Ionic Equations
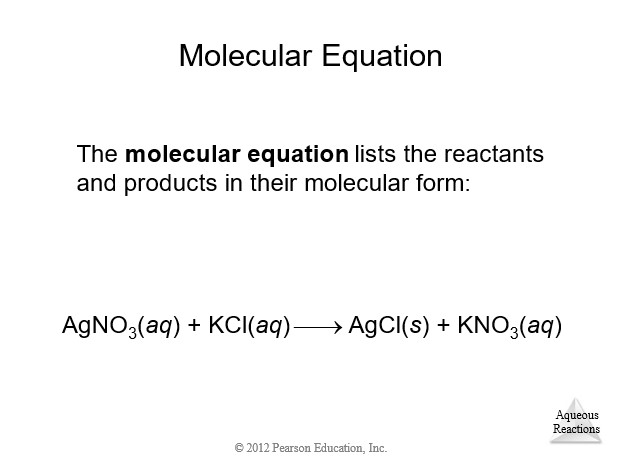

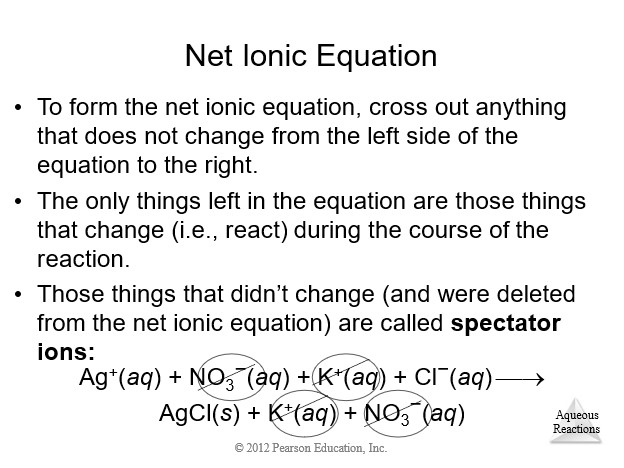

4.3 Representations of Reactions
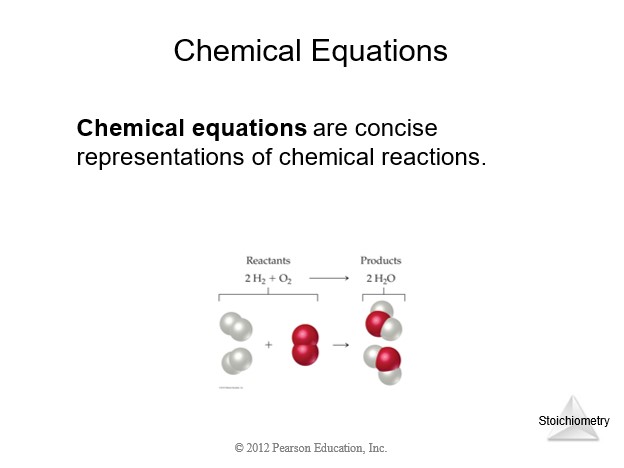
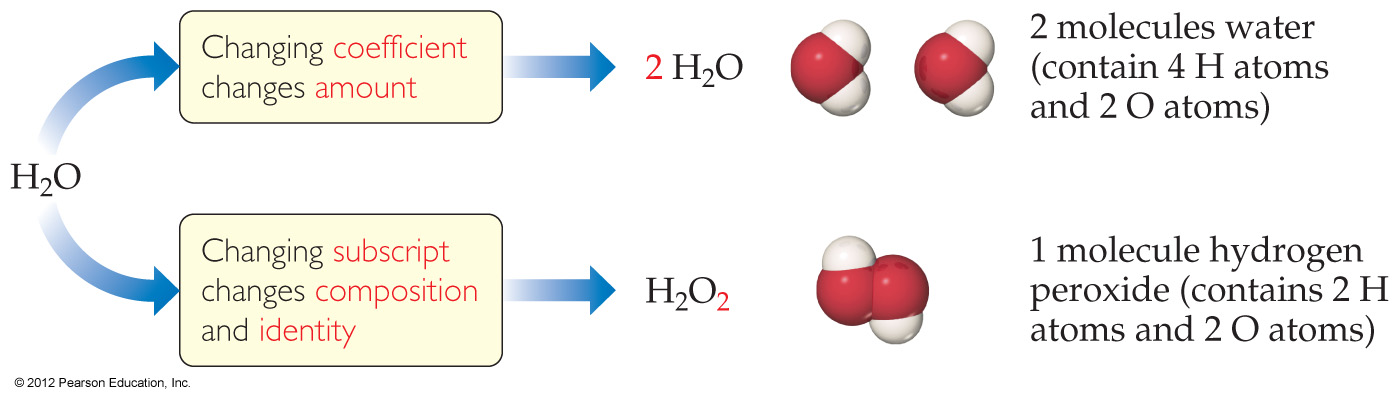
4.4 Physical and Chemical Changes

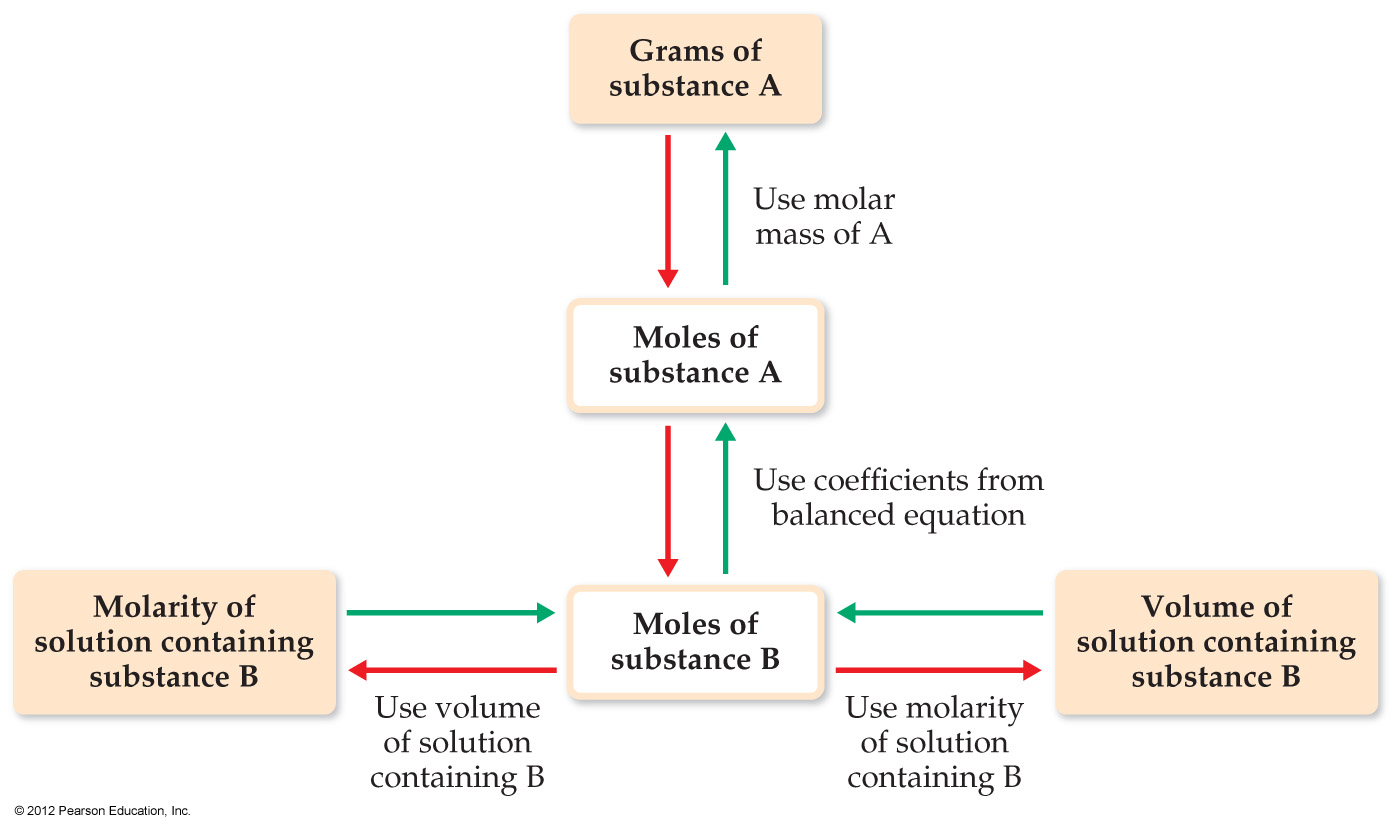
4.5 Stoichiometry
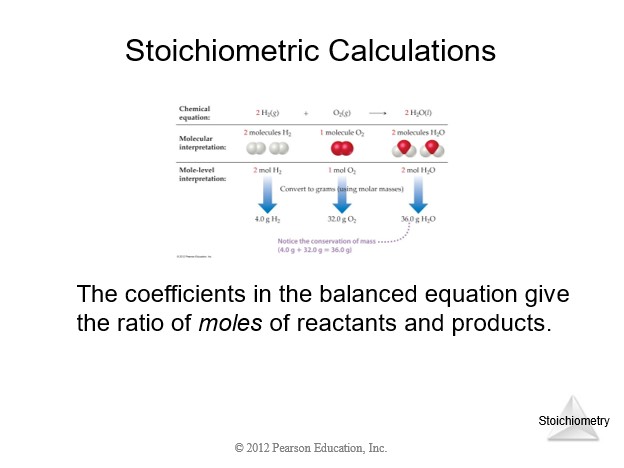
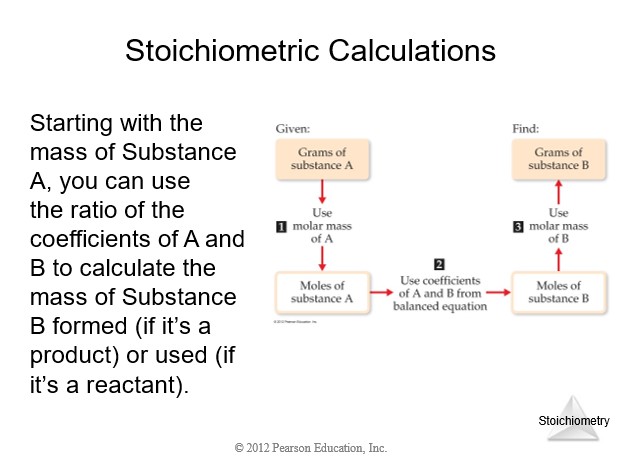
| Stoichiometry of Balanced Chemical Equation | |
| 0. Balanced chemical equation. | |
| 1. Given quantity and units. | |
| 2. Conversion from given units to moles. | |
| 3. Mole ratio between required and given quantities (coefficients from balanced chemical equation). | |
| 4. Conversion from moles to required units. | |
| 5. Calculate the requested quantity. |
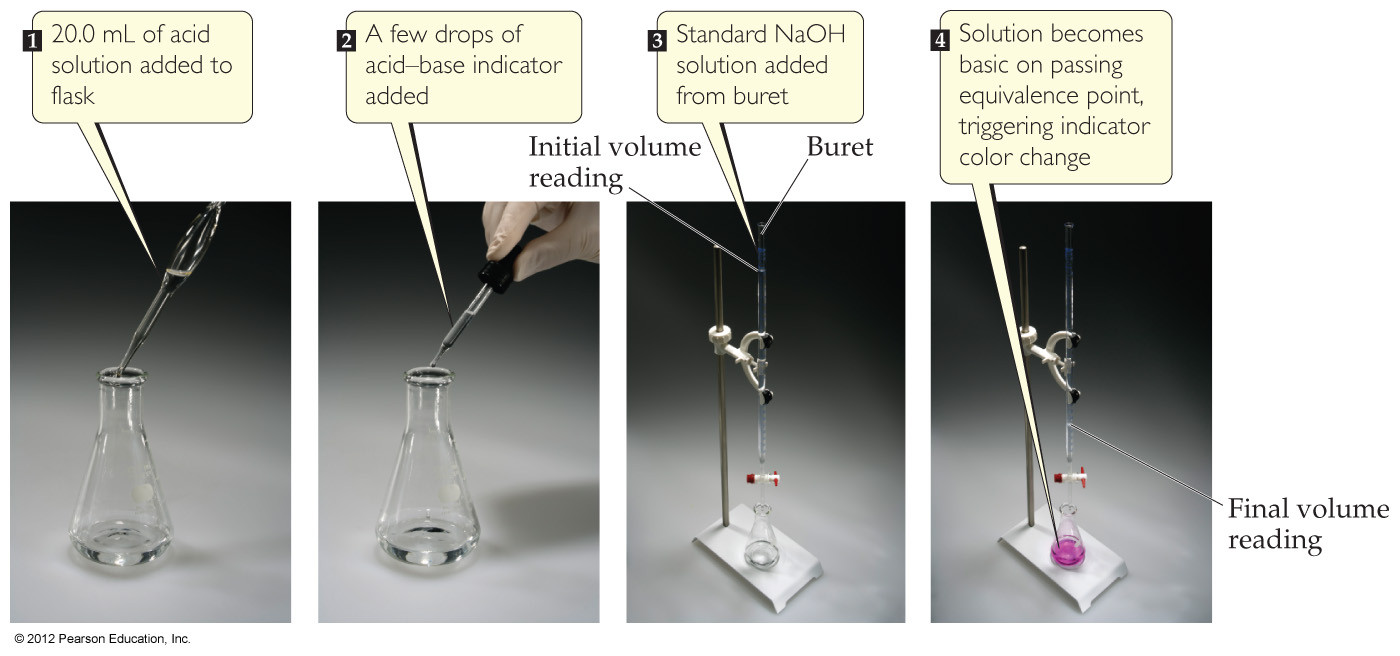
4.6 Introduction to Titration
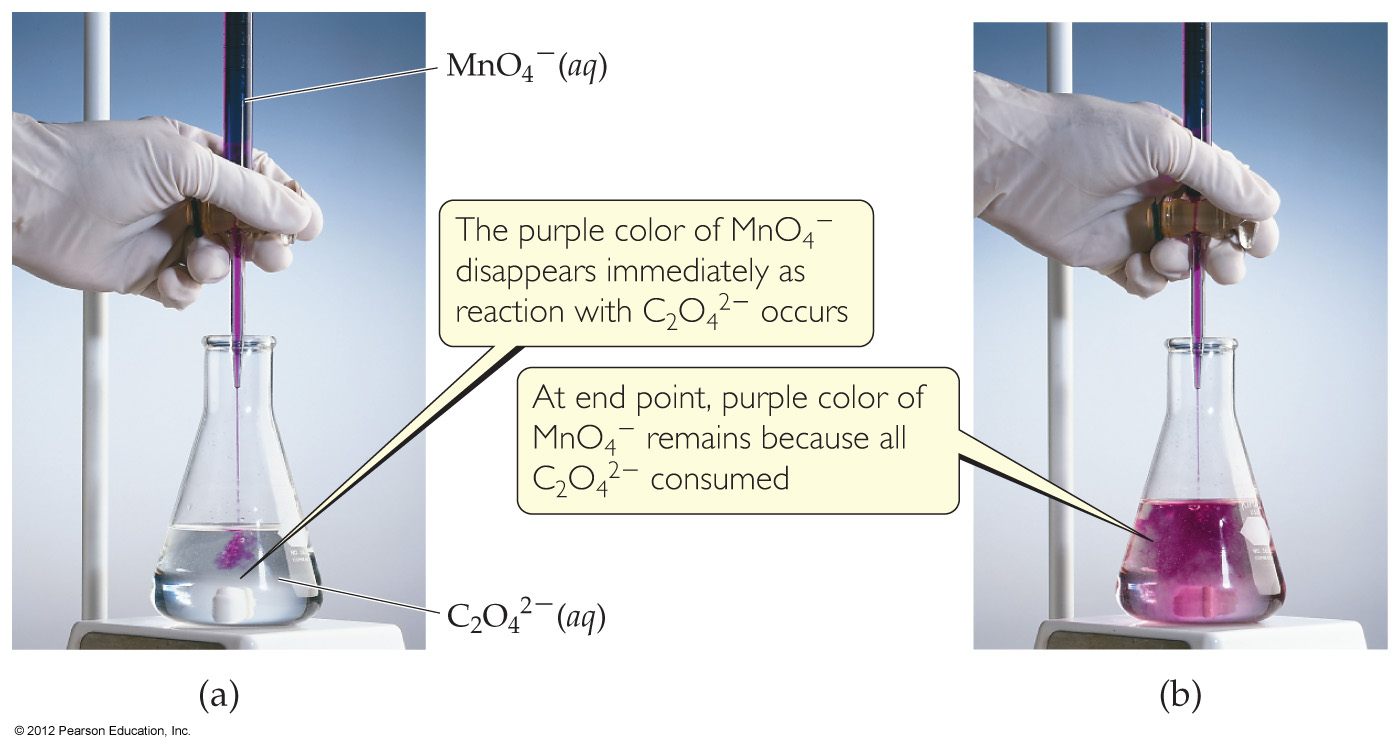
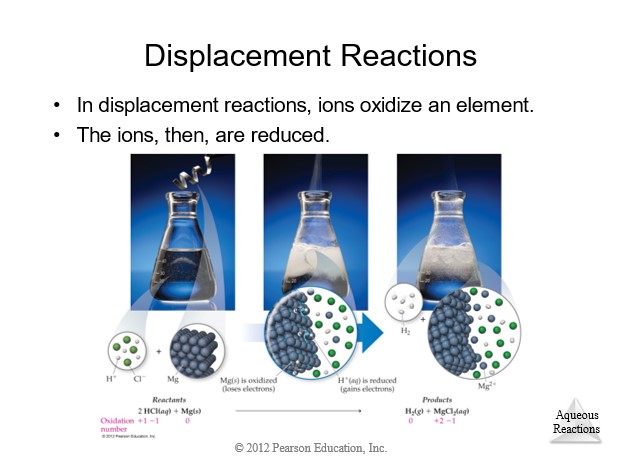
4.7 Types of Chemical Reactions
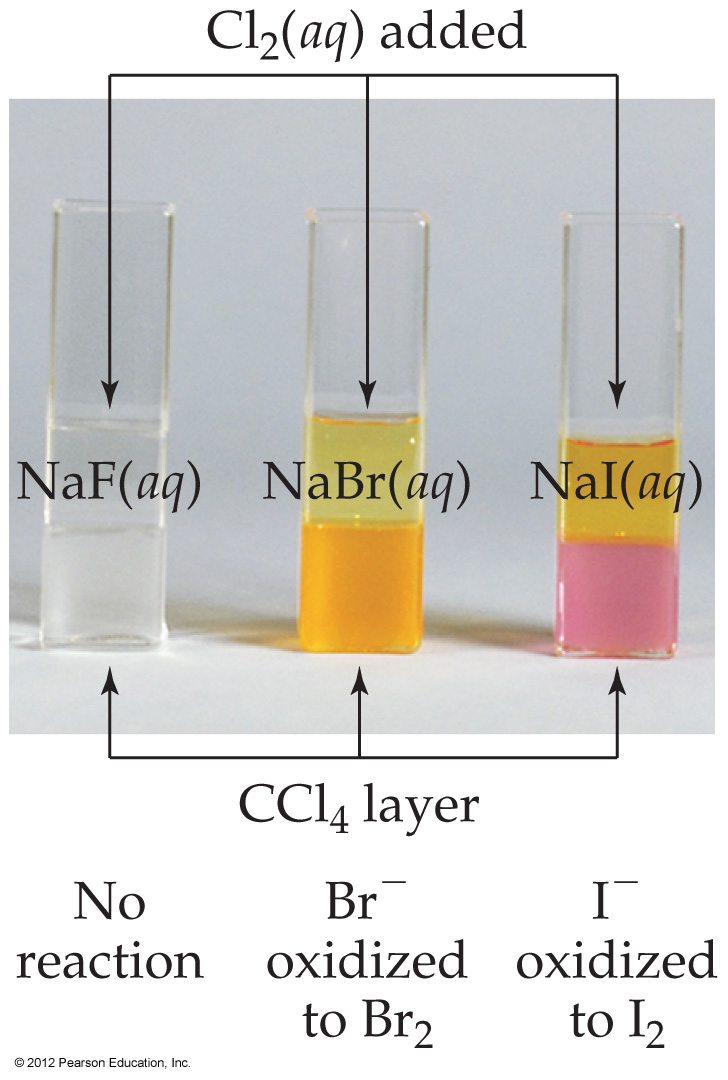
| F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 |
|---|
| 2HI + Br2 → 2HBr + I2 |
| 2HBr + Cl2 → 2HCl + Br2 |
| 2HCl + F2 → 2HF + Cl2 |

 reactions.jpg)
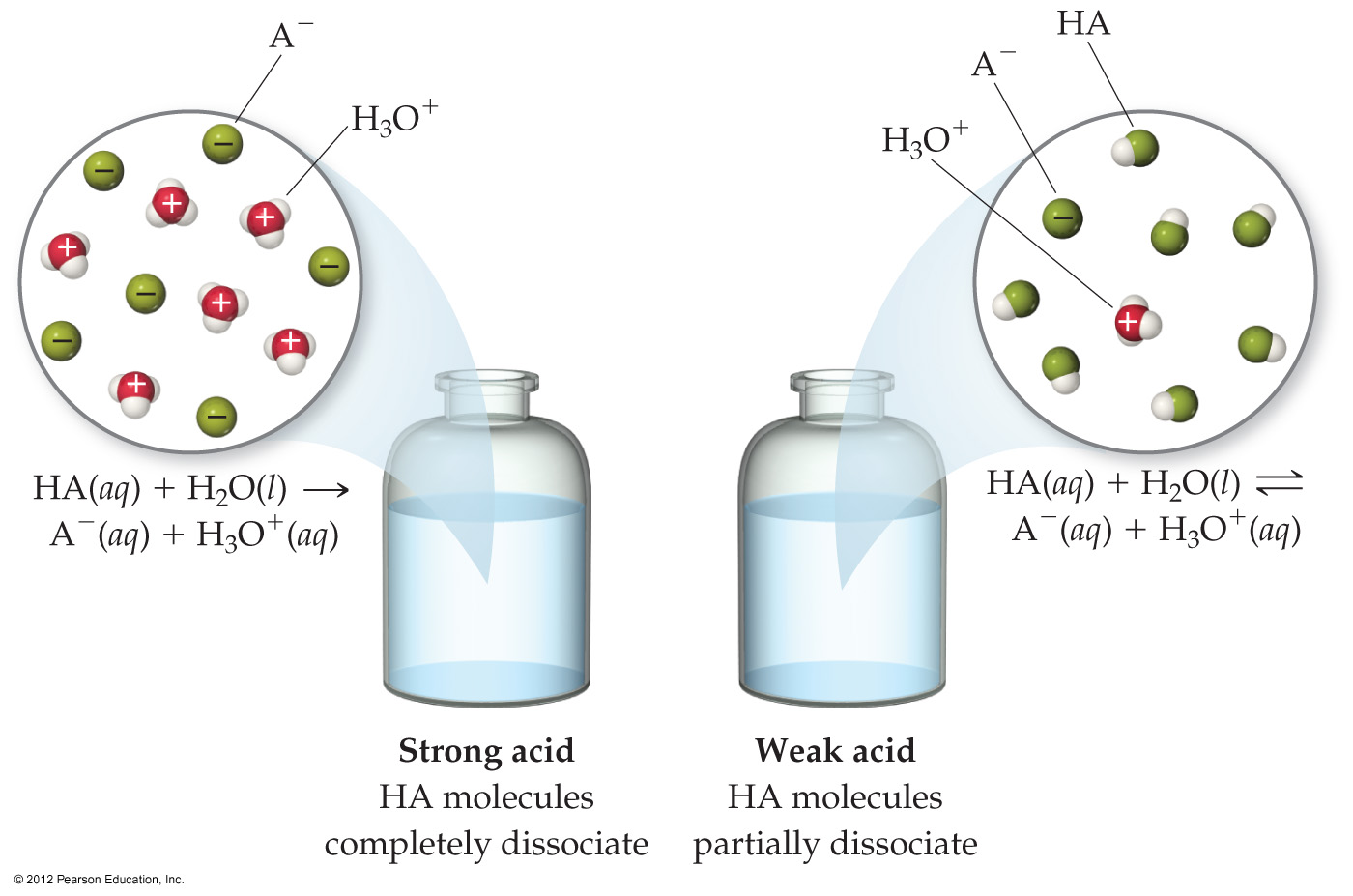
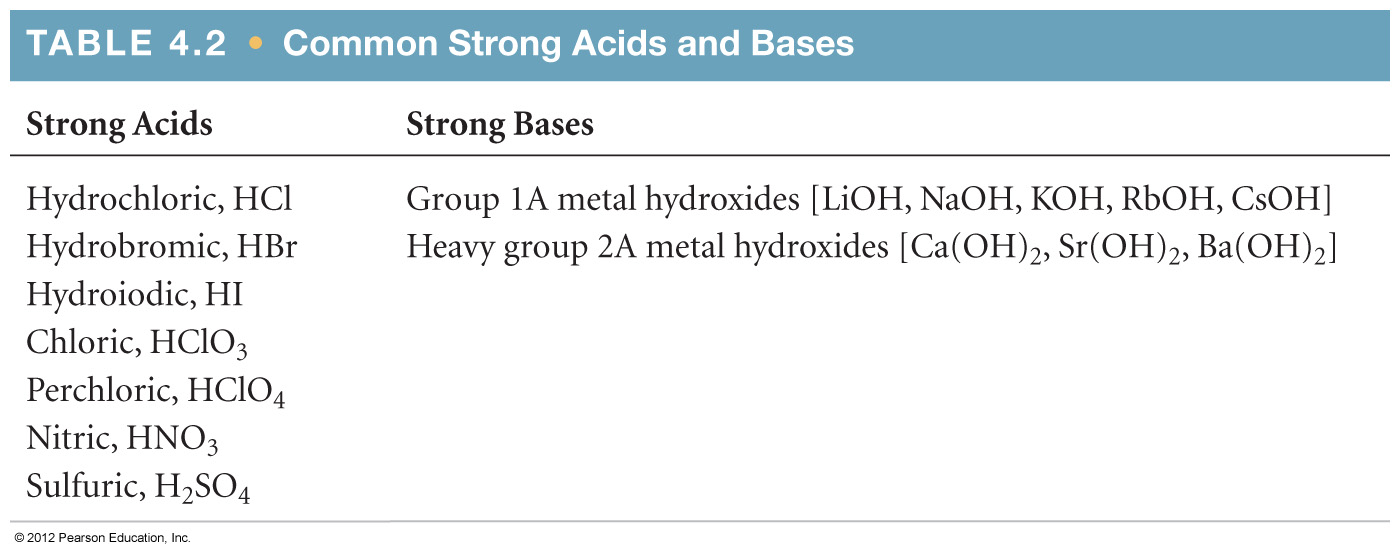
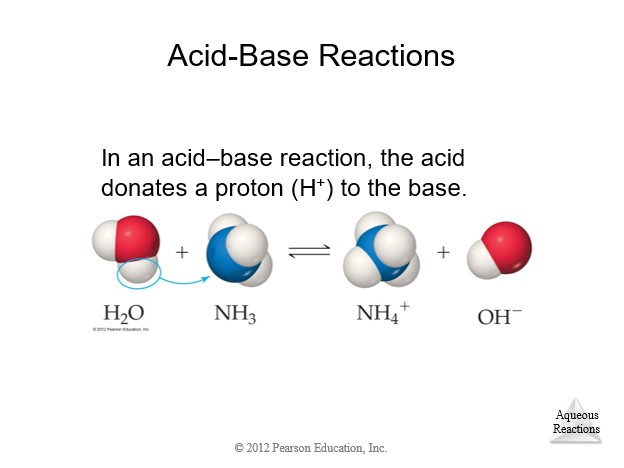
4.8 Introduction to Acid-Base Reactions


4.9 Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions
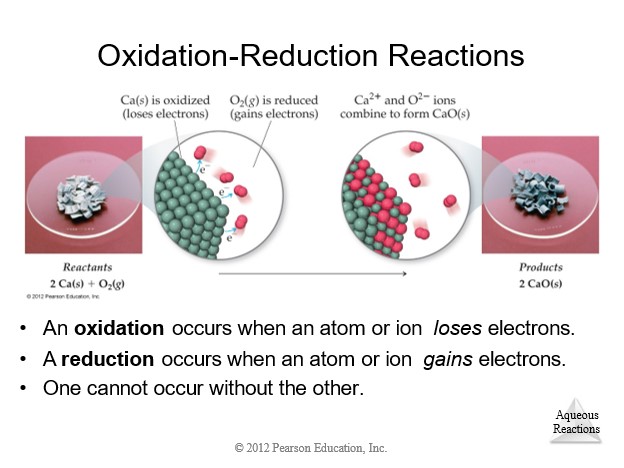
|
Assigning Oxidation States (OS) |
|
1. An element in a free form has OS = 0. |
|
2. In a compound or ion, the sum of the oxidation states equals the total charge of the compound or ion. |
|
3. Fluorine in compounds has OS = −1; this extends to chlorine and bromine only when not bonded to a lighter halogen, oxygen or nitrogen. |
|
4. Group 1 and group 2 metals in compounds have OS = +1 and +2, respectively. |
|
5. Hydrogen has OS = +1 but adopts −1 when bonded as a hydride to metals or metalloids. |
|
6. Oxygen in compounds has OS = −2 but only when not bonded to oxygen (e.g. in peroxides) or fluorine. |
|
-Thanks Wikipedia |
| Reaction Type | Redox? | Model | Guidelines |
| Synthesis/Combination | Maybe | A + B → C | - |
| Decomposition | Maybe | C → A + B | - |
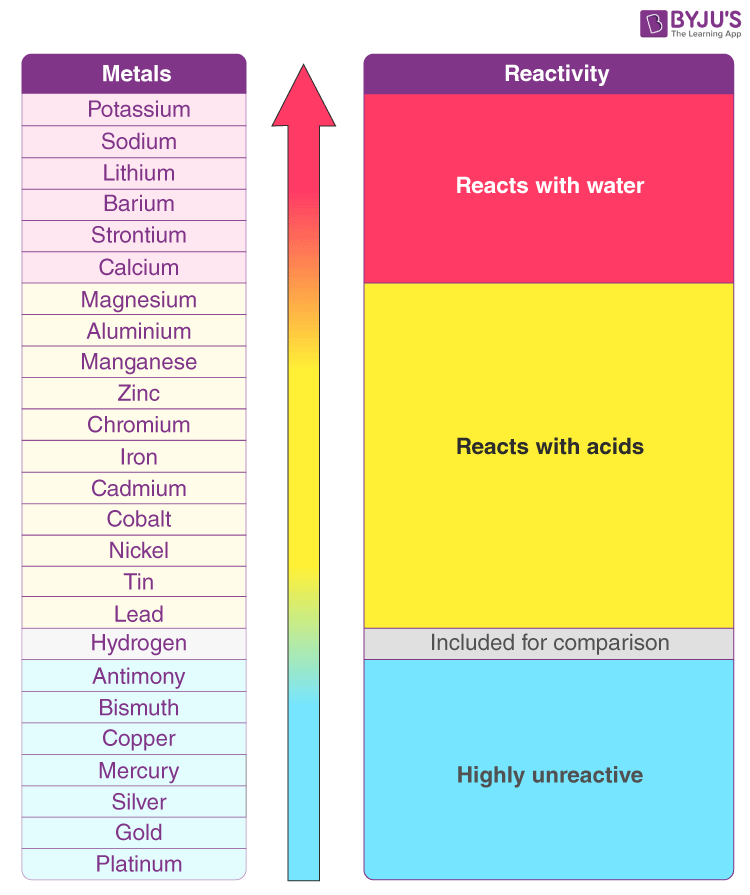
| Single Displacement | Always | AB + C → AC + B | Activity Series (metals or halogens) |
| Double Displacement (Metathesis/Exchange) | Never | AB + CD → AD + CB | Solubility Table, Acid-Base Reactions (with or without gas), Complex Table (Metals and Ligands) |
| Combustion (Complete) | Always | CHO + O2 → CO2 + H2O | Principle reactant is any compound of C and H, and sometimes O. Products are always CO2 and H2O. |
| Combustion (Incomplete) | Always | CHO + O2 → CO + H2O | Products vary in an incomplete combustion reaction, but "half-way" is with CO and H2O products. |
Copyright© 2024 Chemical Solutions
bvins@mrvins.com